Peptide therapy within the NL-Peptides line may raise numerous questions. This article has been prepared to address key issues related to dosing, the potential benefits and limitations of NL-PEPTIDES, as well as the concurrent use of multiple peptides.
Keywords: NL-Peptides; peptides; NL-BPC-157; NL-Epithalon; NL-GHK-Cu; administration protocol; limitations of use; benefits of use
NL-PEPTIDES
In response to challenges associated with producing peptides that can reach the intestine intact, we developed a new class of peptides referred to as NL-peptides, also described as next-generation peptides. The properties of these pharmaceutically active peptides reflect their advantages over conventional peptides. They are characterised primarily by extended stability and resistance to pH and temperature changes, both during product storage and within the gastrointestinal environment. Consequently, following capsule ingestion and transport to the small intestine, the peptide is not degraded.
NL-peptides are also distinguished by their ability to mimic naturally occurring proteins and by high metabolic stability. As a result, NL-peptides—acting in a manner similar to endogenous proteins—can be absorbed from the intestinal tract in an intact form and are not degraded during the absorption process.
POSITIVE ASPECTS OF PEPTIDE USE
Our NL-PEPTIDES series demonstrates a broad spectrum of activity, which is outlined below for each peptide.
NL-BPC-157
NL-BPC-157 is described as exhibiting neuroprotective and antidepressant-like activity, supportive effects during withdrawal syndromes related to long-term medication use, and potential assistance in mitigating certain consequences associated with substance dependence. It supports gastrointestinal function in conditions such as gastric mucosal inflammation, gastric ulcers, gastro-oesophageal reflux disease, leaky gut syndrome, and gastrointestinal complications related to the use of other medications. It is described as exerting a protective effect on the stomach and the gastrointestinal tract in the context of medication use, dietary factors, and injury.
It is further presented as supporting skin regeneration in wounds, burns and cuts, and as facilitating recovery of the musculoskeletal system following fractures and injuries involving bones, muscles, tendons and joints. Additionally, NL-BPC-157 is described as supportive in the course of cardiovascular conditions, including arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis, varicose veins and diabetes, and as mitigating harmful impacts of various factors on the heart and cardiac function.
The peptide is also presented as supportive in selected dermatological conditions (e.g., folliculitis, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, skin necrosis and rosacea). Moreover, it is described as beneficial in conditions such as urinary incontinence, vesicovaginal fistula, and scrotal injury, while providing a protective effect on the urinary tract and kidneys. NL-BPC-157 is also described as reducing inflammatory processes and alleviating pain, supporting immune function, and aiding recovery from injuries in athletes and physically active individuals.
NL-GHK-Cu
NL-GHK-Cu is described as having anti-wrinkle activity, reducing hyperpigmentation, and alleviating or improving dermatological conditions such as acne, eczema and psoriasis. It is presented as increasing skin firmness, elasticity and thickness, improving the condition, thickness and resilience of hair and nails, and supporting skin regeneration by accelerating healing of both minor injuries (cuts, minor cosmetic procedures) and larger wounds (post-operative wounds, invasive cosmetic procedures).
It is additionally described as reducing the appearance of scars (including post-operative and post-acne scars), hyperkeratosis and skin thickening, and limiting hair loss. Furthermore, NL-GHK-Cu is presented as alleviating pulmonary infections and lung damage while improving breathing quality and immune function, reducing systemic inflammation and pain. Preventive effects are also described in conditions such as atherosclerosis, cancer, cataract, diabetes, nephropathy and Alzheimer’s disease.
NL-Epithalon
NL-Epithalon is described as supporting slowing of biological ageing and promoting longevity, reducing stress responses, maintaining visual function, improving circulation and supporting normal blood pressure, delaying age-related changes and dementia-associated symptoms (including memory decline, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and Huntington’s disease), supporting mobility, and maintaining healthy, elastic and firm skin while reducing skin lesions, rashes and acne.
It is also presented as reducing risks associated with joint disease and osteoporosis, supporting normal metabolism and weight management, increasing and maintaining physical endurance, reducing insomnia and improving sleep quality and duration. Additionally, it is described as having preventive potential in maintaining oral health, as well as supportive use in dental restoration.
Summary of described areas of support
NL-BPC-157 is described as supporting/improving/restoring the function of:
- the nervous system
- the gastrointestinal system
- the musculoskeletal system
- the cardiovascular system
- the skin
- the urogenital system
- pain management
- regenerative processes in physically active individuals
- the immune system
NL-GHK-Cu is described as supporting/improving/restoring the function of:
- vision
- gene regulators
- healthy skin condition
- the immune system
- skin regenerative processes
- anti-ageing processes
- anti-inflammatory processes
- anti-cancer processes
NL-Epithalon is described as supporting/improving/restoring the function of:
- the nervous system
- the cardiovascular system
- the musculoskeletal system
- the visual system
- gene regulators
- healthy skin condition
- metabolic processes
- brain processes
- anti-ageing processes
- anti-cancer processes
NEGATIVE ASPECTS OF PEPTIDE USE
Peptides are described as not causing a range of adverse effects. When used regularly and consistently, they are presented as not leading to dangerous or permanent changes in health or overall physical condition.
| NL-PEPTIDES | Recommended single dose / daily portion |
|---|---|
| NL-BPC-157 | 200–400 mcg daily (1 or 2 capsules) |
| NL-GHK-Cu | 2 mg daily (1 capsule) |
| NL-Epithalon | 1 mg daily (3 capsules) |
LIMITATIONS OF PEPTIDE USE
The only generally recognised limitation of peptide use concerns the target groups that include children, pregnant women, and breastfeeding mothers.
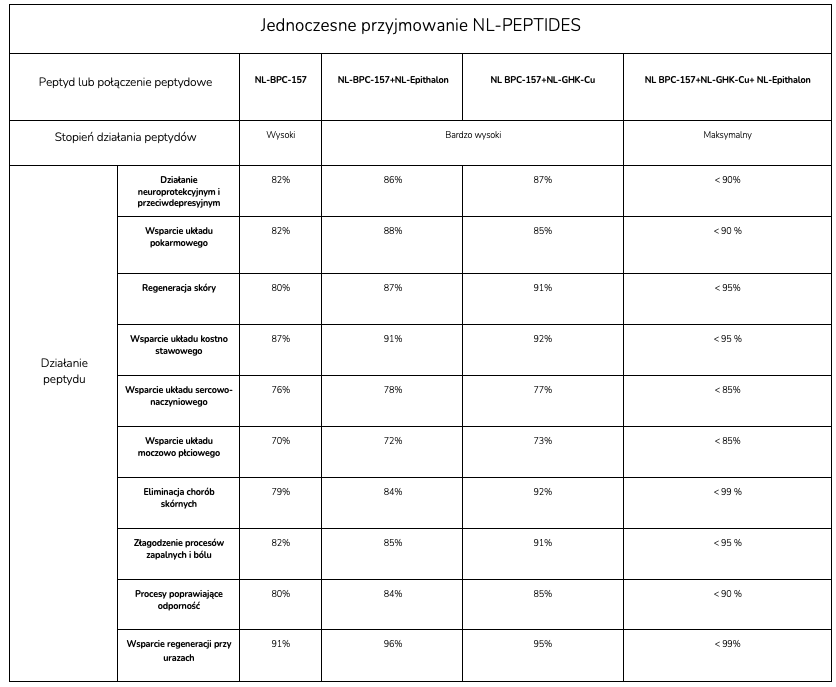
CONCURRENT USE OF MULTIPLE PEPTIDES
The concurrent use of several peptides is described as not producing adverse effects; on the contrary, in certain conditions it is presented as providing the broadest possible activity profile, delivering the best and most durable outcomes.





NL-Epithalon in the anti-obesity therapy
NL-Epithalon in the anti-obesity therapy