Abstract: BPC-157 therapy is used in the world of sport and physical activity not only for its regenerative function, but also for its protective, analgesic, anti-inflammatory and anti-oedema properties. The wide range of applications of this therapy allows it to be implemented as a therapeutic, preventive and supportive treatment for acquired sports injuries or increased physical activity.
Keywords: sports injuries; sports damage; physical activity; musculoskeletal system; microtraumas; lateral patellar impingement, BPC-157 therapy; ankle joint; patella; anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) damage; medial meniscus damage; patellar ligament overload; joint injuries; Bennett fracture; Achilles tendon injury; muscle injuries; muscle strain; muscle tear; spinal injuries; shoulder joint degeneration; lateral curvature of the spine in the lumbar and thoracic regions; chest injury; rib contusion; prevention
List of abbreviations: BPC - body protection compound;
Sports injuries and damage
The risk of sports injuries is an inherent part of any physical activity. Injuries and damage in sport are usually associated with excessive strain during physical exertion. Both professional athletes practising specific sports and amateur athletes are at risk of injury, especially when they do not have sufficient knowledge of how to practise a given activity. Proper conduct during sports is important because only skilfully performed exercises can bring effective results. Unfortunately, it is rare to avoid injuries and damage when practising any sport. When practising physical activity, both intensive movement improvement and muscle strength increase are not without side effects, resulting in accelerated tissue wear, especially in professional athletes, where excessive exploitation affects areas where tissues are genetically less valuable and susceptible to frequent, cumulative micro-injuries. The alarming increase in the number of injuries and damage to the musculoskeletal system in physically active people can lead to serious dysfunction, which is why it is so important to provide appropriate treatment or prevention at the stage of microtrauma formation, the effects of which will not disappear without proper treatment. In addition, preventive therapy is used in physically inactive individuals, as the human body is subjected to a wide variety of stresses throughout life due to the natural need for movement.
The use of BPC-157 peptide therapy for the most common sports injuries.
Knee joint injuries
The knee joint, as the most functionally and mechanically complex joint in the human body, is also the joint most vulnerable to microtraumas, which lead to dysfunctions causing limited mobility, pain and discomfort in the affected person. As a reminder, the knee joint consists of three bones: the femur, tibia and patella. The muscles surrounding the knee joint are the tensor fascia lata, sartorius, quadriceps femoris, vastus intermedius, vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris and gracilis. Every day, the knee joint is subjected to stress, microtrauma, excessive tension and stretching of the muscles surrounding the joint. It is important in the treatment and prevention of knee joint problems to restore or maintain stability, which ensures correct standing posture. It is also important to include balance and stabilisation exercises and appropriate substances as preventive measures against injuries in all training and physical activities. BPC-157 is one of the substances that have a preventive effect on the ankle joint. Below we present the most common injuries related to knee joint damage and the therapeutic and preventive profile of BPC-157 in the case of these injuries.
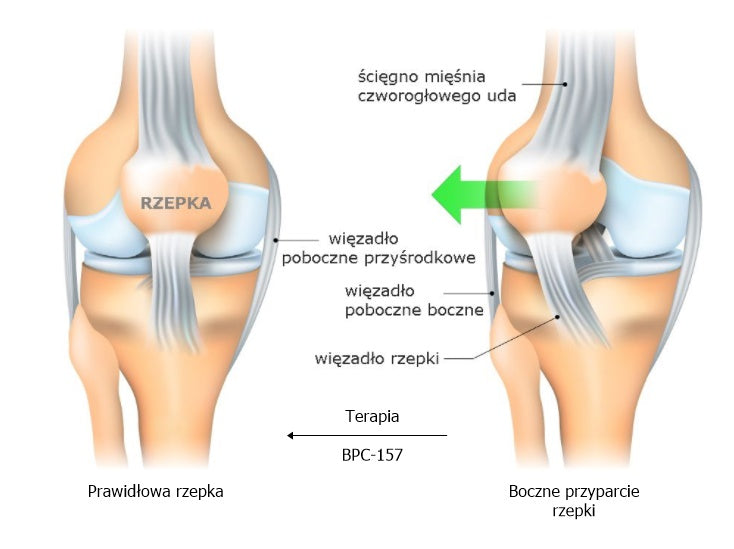
1. Excessive lateral pressure syndrome
An injury known as excessive lateral pressure syndrome is associated with an injury occurring in the patellofemoral joint, which forms the rear part of the patella with the condyles of the femur. The injury results from increased pressure on the lateral condyle of the femur, which disrupts the proper functioning of the patella by causing it to slide incorrectly. In athletes, who often bend their knees, this condition leads to a reduction in physically active life and severe pain. When this injury occurs, it leads to inflammation, muscle weakness and damage to the articular cartilage, which, if not treated properly, can lead to serious degenerative dysfunction. The selection of the appropriate method, symptomatic and preventive treatment leads to a return to physical activity and its maintenance at the previous level.
Therapeutic and prophylactic effects of BPC-157 in cases of lateral patellar impingement
- In mild cases, BPC-157 helps to eliminate anatomical disorders, including ankle valgus deformity.
- In acute cases, treatment includes rehabilitation, supplemented with BPC-157 therapy as an anti-inflammatory and analgesic agent with anti-receptor activity. The peptide antagonises pain through its action on the central dopaminergic system. The analgesic effect of BPC-157 is noticeable at very low doses and within a short time.
In prevention, regular use of the BPC-157 peptide leads to strengthening of the medial head of the quadriceps muscle and reduction of tension in the iliotibial band of the broad fascia of the thigh.

Figure 1. Effectiveness of BPC-157 therapy in cases of lateral patellar impingement
2. Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury
Predisposing factors associated with anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury may include not only the primary cause, which is considered to be the mechanism of anterior cruciate ligament injury with simultaneous knee rotation or rotation on a straight knee, but also gluteus medius muscle weakness or the age of the person engaging in physical activity. The ligaments are most vulnerable to injury at the point of attachment to the femur or tibia. The injury is associated with the occurrence of intra-articular haematoma, joint capsule injury or damage to the general joint surface. The symptoms of this condition include knee instability and may be associated with damage to other joint structures such as the meniscus or tibial collateral ligament. Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury is a dangerous injury, leading to mobility instability and, consequently, the inability to train, accompanied by discomfort and pain. Rapid implementation of therapy is important for correct posture and restoration of desired mobility, especially in competitive athletes. Effective therapy is important in preventing serious conditions that can develop through improper treatment or underestimation of symptoms.
Therapeutic and prophylactic effects of BPC-157 in cases of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury
- In mild cases, BPC-157 helps to eliminate anatomical disorders, including clubfoot.
- In acute cases, treatment includes rehabilitation, supplemented with BPC-157 therapy as an anti-inflammatory and analgesic agent with anti-receptor activity. The peptide antagonises pain through its action on the central dopaminergic system. The analgesic effect of BPC-157 is noticeable at very low doses and within a short time.
In prevention, regular use of the BPC-157 peptide leads to a reduction in the effects of pressure on the affected limb from the side when the joint is slightly bent.
3. Damage to the medial meniscus
An injury such as damage to the medial meniscus occurs during movement in a closed kinematic chain or as a result of previously untreated microtraumas. In most cases, damage to the medial meniscus is accompanied by damage to the cartilage. The injury is most often associated with anatomical abnormalities of the pelvis, resulting in knee valgus. The injury is accompanied by a stabbing, sharp pain in the final phase of knee flexion or locking during extension. Appropriate treatment within a specified time frame is essential for restoring the motor functions of a person who practises sport or physical activity.
Therapeutic and prophylactic effects of BPC-157 in cases of medial meniscus damage
- In mild cases, BPC-157 supports the body's natural regenerative processes through its regenerative potential, acting in the deeper, non-vascularised part of the meniscus.
- In acute cases, treatment includes rehabilitation, supplemented with BPC-157 therapy as an anti-inflammatory and analgesic agent with anti-receptor activity. The peptide antagonises pain through its action on the central dopaminergic system. The analgesic effect of BPC-157 is noticeable at very low doses and within a short time. In advanced stages of injury, surgery may be necessary. The action of BPC-157 will allow for the relief of postoperative pain and the regeneration of both the meniscus itself and the skin damaged by the incision and surgical procedure.
In prevention, regular use of the BPC-157 peptide leads to the alleviation or complete elimination of microtraumas during physical exertion, which lead to the development of the above condition.
4. Overloading of the patellar ligament – ‘jumper's knee’
A characteristic symptom of patellar tendon overload is pain below the patellar tendon, at its apex. As the name suggests, the cause is most often sudden braking of the quadriceps muscle during a jump. The pain experienced during the injury leads to limited physical activity and can vary in intensity, ranging from disappearing pain to chronic and persistent pain.
Therapeutic and prophylactic effects of BPC-157 in cases of patellar ligament overload
- In mild cases, BPC-157 supports natural regenerative processes through its collagenase capabilities, which can make the recovery of a severely damaged knee faster and less painful.
- In acute cases, treatment includes rehabilitation, supplemented with BPC-157 therapy as an anti-inflammatory and analgesic agent with anti-receptor activity. The peptide antagonises pain through its action on the central dopaminergic system. The analgesic effect of BPC-157 is noticeable at very low doses and within a short time. An additional effect promoting the aforementioned collagenase leads to faster regeneration of the damaged patellar ligament.
In prevention, regular use of the BPC-157 peptide leads to a significant reduction in the occurrence of injuries and microtraumas, which leads to broader regenerative processes and, consequently, no exclusion from physical activity for people who practise sport.

Figure 2. Effect of BPC-157 therapy on a condition known as jumper's knee
Joint injuries
Physical activity, especially in the world of sport and excessive physical exertion, can result in joint injury. Joint injuries include fractures, dislocations and sprains. Each injury is accompanied by increasing pain, swelling, bruising or limited mobility, which is why quick and effective therapy is so important to restore our freedom of movement and comfort of life.
1. Bennett fracture
A Bennett fracture is an injury typically seen in athletes. Also known as a boxer's fracture, it affects the first metacarpal bone, where there is a buckling of the metacarpophalangeal joint. Symptoms accompanying this injury include severe pain in the thumb or wrist area. Treatment of this type of injury is complicated and requires rehabilitation. BPC-157 peptide therapy is used here as an additional and supportive therapy.
Therapeutic and prophylactic effects of BPC-157 in Bennett's fracture
- BPC-157, as an anti-inflammatory and analgesic agent, exhibits anti-receptor activity. The peptide antagonises pain through its action on the central dopaminergic system. The analgesic effect of BPC-157 is noticeable at very low doses and within a short period of time.
- The BPC-157 peptide allows broken bones to heal twice as fast. Fibroblasts formed at the fracture site, which create a scaffolding structure made of calcium, cartilage and collagen, develop faster in the presence of the peptide. During bone fracture healing, new tissue is very fragile and delicate, and BPC-157 supports this process, leading to greater strength and hardness and, consequently, faster regeneration and bone healing.
Tendon injuries
Muscle damage or tear is one of the most serious and common soft tissue injuries. This condition occurs in both competitive athletes and people who only practise sport recreationally or sporadically. It most often results from indirect injury, when there is a sudden contraction of the tendon, e.g. during a sudden jump or exertion without prior preparation. Previous inflammation of the tendon is also considered to be a cause of damage. Muscle damage is accompanied by symptoms such as sudden and severe pain, swelling, immobilisation and subcutaneous haemorrhages.
1. Damage to the Achilles tendon
The Achilles tendon, as the heel tendon, is the largest and strongest tendon in our body. In physically active people and professional athletes, it is one of the most commonly torn tendons. Its primary function is to enable flexion of the ankle joint, which is quite important for maintaining physical activity. A tendon rupture is described as a complete break in the continuity of the tendon fibres connecting the muscle to the bone. The direct cause of a tendon rupture is considered to be excessive force acting on a given muscle at a given moment. When the Achilles tendon ruptures, the accompanying symptoms include severe pain, haematoma, limping and rapidly increasing swelling. Complete exclusion from physical activity forces us to undergo immediate treatment and therapy related to the injury.
Therapeutic and prophylactic effects of BPC-157 in cases of Achilles tendon damage
- BPC-157, as an anti-inflammatory and analgesic agent, exhibits anti-receptor activity. The peptide antagonises pain through its action on the central dopaminergic system. The analgesic effect of BPC-157 is noticeable at very low doses and within a short period of time. The peptide helps damaged tendons regenerate faster. Thanks to the action of BPC-157, the recovery period after tendon injury is significantly shorter. BPC-157 therapy reduces swelling in the tendon area and prevents adhesions from forming.
- Preventive, regular use of the peptide is used to protect and regenerate tendons after injury.

Figure 3. Effect of BPC-157 on Achilles tendon regeneration
Urazy mięśni
Muscle injury can be defined in various ways. The most important of these concerns acute damage caused by excessive and sudden pressure on the muscles, most often during physical exertion. Muscle fibres are torn, and the accompanying symptoms, such as pain, loss of strength, swelling or bleeding, prevent us from participating in sports activities and functioning normally. Tendons in the thigh or knee area are most often affected by injuries. On the other hand, prolonged muscle tension causes injuries in the back, groin, legs or arms.
1. Muscle strain
Muscles made up of muscle fibres have the ability to contract and relax, allowing us to perform specific movements. During excessive physical exertion, muscles often become overloaded and strained. This phenomenon causes symptoms such as pain, burning sensation in the muscle, inability to perform certain activities, or limited movement and physical activity. Appropriate regenerative therapy brings the desired results, leading to the restoration of the damaged muscle's function. Preventive therapies are also used in connection with the limited frequency of this type of injury.
Therapeutic and prophylactic effects of BPC-157 in cases of muscle strain
- BPC-157, as an anti-inflammatory and analgesic agent, exhibits anti-receptor activity. The peptide antagonises pain through its action on the central dopaminergic system. The analgesic effect of BPC-157 is noticeable at very low doses and within a short period of time. The peptide helps damaged muscles to regenerate faster. Thanks to the action of BPC-157, the recovery period after muscle injury is significantly shorter.
- Preventive, regular use of the peptide is used to protect and regenerate muscles against injury resulting from prolonged muscle tension.
2. Muscle tear
In the case of a muscle tear, rather than just a strain, the fibres are torn at the moment of maximum overload. Muscle fibre tears most often occur at the point where they connect to the tendon. This injury is accompanied by inflammation and severe pain, which prevents physically active people from participating in sports during their recovery. Appropriate rehabilitation and treatment will help them recover and return to normal physical functioning.
Therapeutic and prophylactic effects of BPC-157 in cases of muscle rupture
- BPC-157, as an anti-inflammatory and analgesic agent, exhibits anti-receptor activity. The peptide antagonises pain through its action on the central dopaminergic system. The analgesic effect of BPC-157 is noticeable at very low doses and within a short period of time. The peptide helps damaged muscle to rebuild more quickly in order to restore muscle function. Thanks to the action of BPC-157, the recovery period after a muscle tear is significantly shorter.
- Profilaktyczne, systematyczne zażywanie peptydu znajduje zastosowanie w ochronie i regeneracji mięśni przed urazem powstającym w wyniku napięcia mięśni przez dłuższy okres czasu.
Urazy kręgosłupa
Spinal injuries are serious injuries that can have various causes. Symptoms accompanying this type of injury include severe, pressing pain, limb paresis, and sensory disturbances. Rapid diagnosis and effective treatment are essential, regardless of the type and cause of the injury. The damage can have serious consequences, including loss of full mobility or the need to give up social, professional or sporting activities.
1. Degeneration of the shoulder joint
Degeneration of the shoulder joint is caused by pathological changes in the cartilage tissue of the shoulder. Over time, the disease can spread to other parts of the shoulder, including bones and tendons. Degenerative injuries occur in athletes and physically active people who put a lot of strain on their shoulders when performing certain activities. In people who are not physically active, degeneration may be caused by work that strains the shoulder area. The injury is characterised by limited range of motion or a feeling of weakness in the limb.
Therapeutic and prophylactic effects of BPC-157 in shoulder joint degeneration
- In the acute phase of degeneration, it is mainly recommended to take medications for shoulder joint degeneration, such as analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs and anti-oedema drugs. The BPC-157 peptide has the aforementioned effects, acting as an anti-inflammatory agent to eliminate inflammation in the body. The peptide antagonises pain through its action on the central dopaminergic system. The analgesic effect of BPC-157 is noticeable at very low doses and within a short time. In addition, BPC-157 therapy reduces swelling in the area of the injury.
- Through its action, the BPC-157 peptide creates a specific protective and regenerative barrier. When used prophylactically, both in injectable and oral form, it minimises the occurrence of shoulder joint injuries or alleviates the symptoms that occur when they do occur.

Figure 4. BPC-157 therapy for shoulder joint degeneration
2.Boczne skrzywienie kręgosłupa w odcinku lędźwiowym i piersiowym
Lateral curvature of the spine is most commonly found in professional athletes and people who engage in intense training and sports activities. Improper training can lead to this injury, causing curvature of the aforementioned sections, as well as elevation of the lower angle of the right shoulder blade and excessive tension in the neck and shoulder muscles. All of these processes can cause body asymmetry with simultaneous balance disorders and accompanying pain when performing certain physical activities. Untreated or underestimated symptoms can lead to more serious consequences, including muscle rupture or elimination from physical activity.
Therapeutic and prophylactic effects of BPC-157 in cases of lateral curvature of the spine in the lumbar and thoracic regions
- BPC-157, as an anti-inflammatory and analgesic agent, exhibits anti-receptor activity. The peptide antagonises pain through its action on the central dopaminergic system. The analgesic effect of BPC-157 is noticeable at very low doses and within a short period of time.
- Thanks to its regenerative properties, the BPC-157 peptide creates a scaffolding structure made of calcium, cartilage and collagen, which leads to faster regeneration of spinal degeneration.
Urazy klatki piersiowej
Chest injuries often occur as a result of sports injuries due to the discipline practised. These injuries most often involve the ribs, which are the first to be exposed to injury. Chest injuries are most often accompanied by pain and difficulty breathing when coughing, taking a deep breath, and moving the lower limbs.
1. Rib contusions
Bruised ribs are a common symptom of excessive physical exertion or aggressive sports. Bruised ribs can cause shortness of breath, difficulty moving, or bruising at the site of the injury. Recovery from bruised ribs is important if you want to return to physical activity quickly.
Therapeutic and prophylactic effects of BPC-157 in cases of rib fractures
- BPC-157 jako środek przeciwzapalny i przeciwbólowy wykazuje działanie anty receptorowe. Dzięki działaniu peptydu dochodzi do antagonizacji bólu, które opiera się na działaniu poprzez centralny układ dopaminergiczny. Działanie przeciwbólowe BPC-157 zauważalne jest w bardzo małej dawce i w krótkim czasie;
- Dzięki właściwościom regeneracyjnym peptyd BPC-157 pozwala na szybszą rekonwalescencję oraz zmniejszenie zasinień i powstałych obrzęków w miejscu urazu.
Prevention of sports injuries
Prevention of sports injuries is an important but also very complex process that requires a multidisciplinary approach from people who engage in physical activity professionally or even recreationally. In the case of athletes, it is important to remain physically active for as long as possible in order to extend their sporting careers and increase their motor potential. Preventive measures can be divided into three levels, which also include BPC-157 peptide therapy. Primary prevention is characterised by a reduction in the likelihood of injury and health problems, resulting in the prevention of injury, while secondary prevention involves halting the development of the negative effects of injury. The third level of prevention, which is the final level, aims to prevent the effects of past injuries, counteract their recurrence and minimise secondary damage and complications. BPC-157 peptide therapy is used in all these stages, demonstrating its protective effects thanks to, among other things, its ability to regenerate microtraumas leading to more serious changes and as a substance that creates a specific protective barrier for the musculoskeletal system.
Summary
Given the broad spectrum of action of the BPC-157 peptide, therapy with this peptide can be safely recommended primarily to competitive athletes, but also to people who engage in physical activity and those who do not, due to the fact that our musculoskeletal system, unfortunately, undergoes spontaneous damage during basic daily activities. Its regenerative, analgesic, anti-inflammatory and anti-oedema effects have found a wide range of applications in the treatment, elimination and minimisation of sports injuries. It is safe to say that BPC-157, not only in injectable form but also in oral form, is a precursor and a modern essential for people who engage in less or more physical activity.
Bibliography
1.Grygorowicz. M, Głowacka.A, Kompleksowa ocena fizjoterapeutyczna podstawą profilaktyki pierwotnej urazów sportowych. 2010, 79, 3, 240–244
2.D.Perovic, D.Kolenc, V.Bilic, N.Somun, D.Drmic, E.Elabjer, G.Buljat, S.Seiwerth, P.Sikiric, Stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 can improve the healing course of spinal cord injury and lead to functional recovery in rats. 2019; 14: 199; DOI:10.1186/s13018-019-1242-6
3.T.Huang,K.Zhang,L.Sun,X.Xue,C.Zhang,Z.Shu,N.Mu,J.Gu,W.Zhang, Body protective compound-157 enhances alkali-burn wound healing in vivo and promotes proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis in vitro. 2015; 9: 2485–2499; DOI:10.2147/DDDT.S82030
4.Kraszewski.K, Drogi życiowe sportowców po urazach uniemożliwiających dalszą karierę - aspekty psychologiczne. DOI: https://doi.org/10.32626/2309-8082.2013-0.%25p





Pain management. Analgesic use of BPC-157 peptide therapy
The effect of BPC-157 therapy on the immune system