NL-GHK-Cu peptide therapy for the most common lung diseases and injuries. The protective role of the peptide allows for the maintenance of a properly functioning respiratory system.
Abstract: Nearly half of the processes occurring in cells cannot take place without oxygen. Unfortunately, the body cannot store it. Therefore, the respiratory system must constantly supply cells with this life-giving gas, which is why it is so important to maintain a healthy and properly functioning respiratory system. The NL-GHK-Cu peptide, which is a safe and non-toxic peptide, has the ability to activate many pathways that can be used in therapy to alleviate the symptoms of respiratory diseases, particularly those affecting the lungs. In addition, therapy with the NL-GHK-Cu peptide allows for the maintenance of a healthy and properly functioning respiratory system and all its components. Keywords: NL-GHK-Cu; respiratory system; lungs; lung diseases; bronchitis; pneumonia; asthma; tuberculosis; COPD; therapy; respiratory failure; lung damage; pulmonary fibrosis; protection; gas exchange
Introduction
It is known that NL-GHK-Cu peptide, being a naturally occurring peptide, is safe, non-toxic, and has a broad spectrum of activity. It is released in the body during trauma, which is why we can gradually use it in therapy both to protect the respiratory system and to support the regeneration of its components, especially the lungs, as they are affected by most of the common diseases within this system.
STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
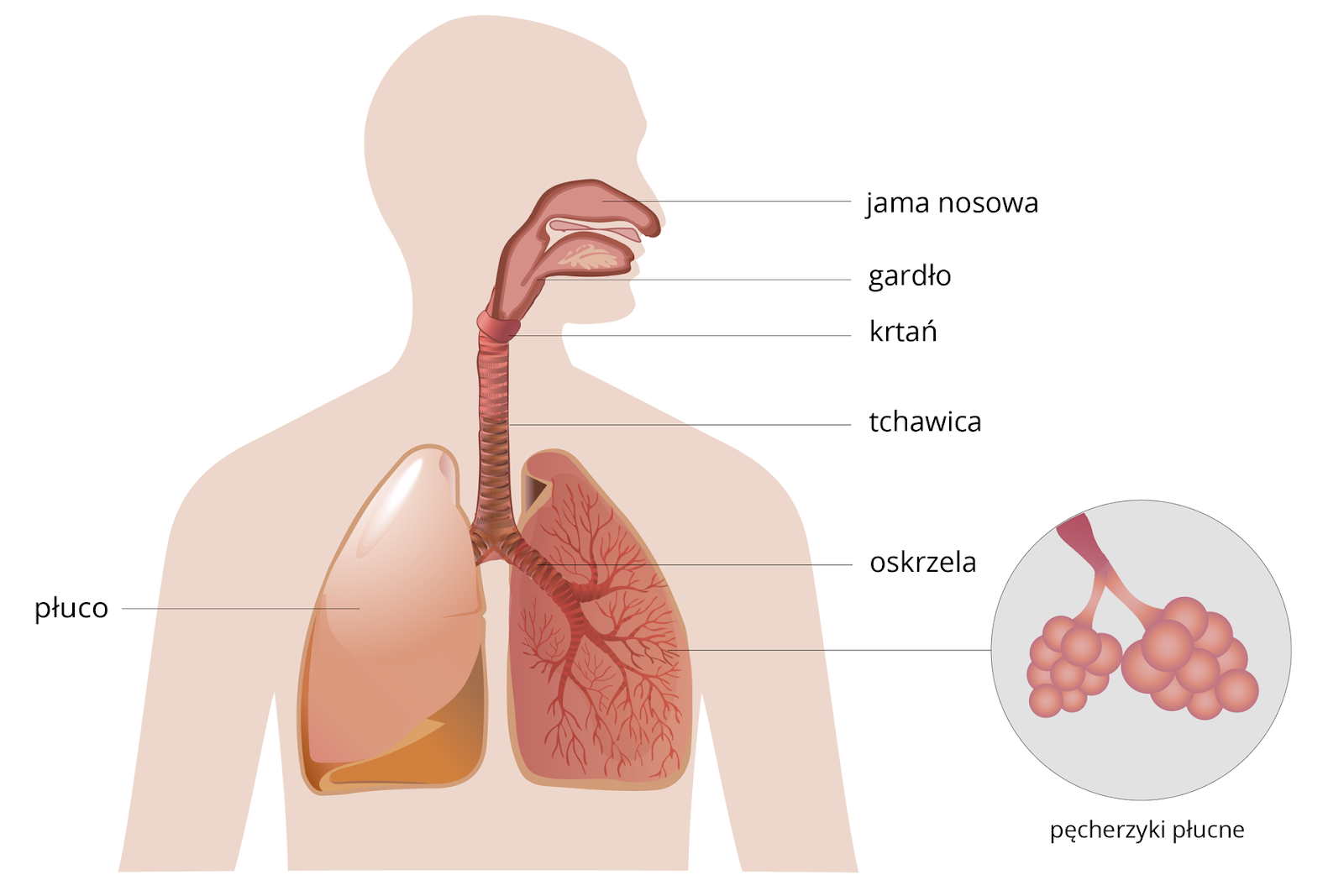
The respiratory system consists of the upper and lower respiratory tract and the gas exchange organ, i.e., the lungs. The upper respiratory tract includes the nasal cavity and throat. The lower respiratory tract includes the larynx, trachea, and bronchi. The lungs are the main respiratory organs. In addition, the respiratory system includes respiratory muscles such as the diaphragm, external and internal intercostal muscles, and accessory respiratory muscles.

RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS
The respiratory system ensures the efficient intake and transport of respiratory gases, i.e., oxygen and carbon dioxide, as well as gas exchange, which involves taking oxygen from the lungs into the blood and expelling carbon dioxide from the blood into the lungs and then further through the respiratory tract outside the body. Each element of the respiratory system has its own specific function: the nasal cavity cleans, warms, and humidifies the inhaled air; the larynx enables the production of sound; in the case of the trachea, it is the transport of air to the bronchi, and in the case of the main bronchi, it is the ability to deliver air to the alveoli. Focusing on the important process of gas exchange, the bronchi are divided into smaller and smaller branches ending in alveoli. Oxygen passes from the alveoli into the blood. It travels with the blood throughout our body and reaches all of its cells. Carbon dioxide, on the other hand, passes from each cell into the blood. It is transported to the lungs, where it passes from the blood into the alveoli. It is then removed from the alveoli along with the exhaled air. Both processes, i.e., the uptake of oxygen into the blood and the removal of carbon dioxide from it, occur simultaneously.
LUNGS
The lungs are shaped like large, spongy, and elastic sacs. They are gas exchange organs located in the chest. They are protected on the outside by a thin double membrane called the pleura, which is filled with a small amount of fluid. This prevents damage to the lungs due to friction against the ribs and other bones of the chest during breathing movements. Inside the lungs, the bronchi branch out like a tree, forming a system of increasingly smaller tubes called bronchioles. At their ends are the alveoli. The alveoli are surrounded by a dense network of capillaries. Gas exchange takes place between them and the air coming from the alveoli by diffusion. The transfer of oxygen into the blood and carbon dioxide from the blood into the alveoli is very fast and efficient thanks to three basic aspects: 1. The walls of the alveoli and capillaries are made up of a thin, single layer of flat epithelium. 2. The network of capillaries covering the alveoli is very dense. 3. The alveoli form a very large surface area for gas exchange.
LUNG DISEASES
Proper functioning of the respiratory system is essential for maintaining the health and well-being of the entire body. Unfortunately, the number of people affected by lung diseases caused by various factors, including environmental, genetic, and lifestyle factors, is growing every year. The most commonly diagnosed lung diseases, apart from cancer, include sarcoidosis, cystic fibrosis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
| Symptoms | Cause | Treatment/Therapies |
|
| Bronchitis |
|
|
|
| Asthma |
|
|
|
| Pneumonia |
|
|
|
| Tuberculosis |
|
|
|
GHK-CU IN LUNG DISEASES
The NL-GHK-Cu peptide, which is a safe and non-toxic peptide, has the ability to activate multiple pathways that enable its use in therapies that alleviate the symptoms of respiratory diseases, particularly those affecting the lungs. In addition, therapy with the NL-GHK-Cu peptide helps maintain a healthy and properly functioning respiratory system and all its components.
GHK-CU THERAPY IN CASES OF ACUTE LUNG INJURY AND RESPIRATORY FAILURE
Acute lung injury (ALI), along with its most severe form, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), is a disorder of acute inflammation and tissue damage characterized by loss of alveolar-capillary membrane integrity, excessive migration of transendothelial neutrophils, and the release of proinflammatory and cytotoxic mediators, leading to lung damage, which may result in respiratory failure, among other consequences. NL-GHK-Cu peptide therapy: Studies have shown that NL-GHK-Cu peptide therapy reduced the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and increased superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity while reducing the production of TNF-α and IL-6 by suppressing NF -κB p65 and p38 MAPK signaling, thereby attenuating histological changes in the lungs caused by damage and suppressing the infiltration of inflammatory cells into the lung parenchyma, resulting in the alleviation of lung damage and the elimination of inflammation. In addition, the NL-GHK-Cu peptide supported regenerative processes after inflammation.
GHK-CU THERAPY FOR PULMONARY FIBROSIS
Pulmonary fibrosis is a condition that usually affects older people as a result of their lifestyle, but symptoms of this condition can also be recognized in children. There are many factors that predispose people to pulmonary fibrosis. The most common causes include smoking, exposure to harmful dust, environmental factors, and certain medications. NL-GHK-Cu peptide therapy: The GHK peptide itself, without the copper component, has been used in degenerative neuropathies and disorders by suppressing the peroxidation process. In combination, the NL-GHK-Cu complex, thanks to the attached metal ion, activates superoxide dismutase (SOD), which is dependent on Cu and Zn, promoting endogenous antioxidant activity. The NL-GHK-Cu complex reduces oxidative damage by inhibiting inflammation and reducing the release of ferritin iron in damaged tissues. Additionally, NL-GHK-Cu reduces the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), increases SOD activity, and simultaneously reduces the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines in acute lung injury caused by fibrosis.
GHK-CU THERAPY IN COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a respiratory condition, the causes of which are most often environmental. Patients suffering from COPD experience symptoms resulting from impaired airflow through the lungs. The disease itself has a poor prognosis, which is why it is important to diagnose it quickly and, consequently, to start appropriate treatment and supportive therapy. NL-GHK-Cu peptide therapy: The NL-GHK-Cu complex has been shown to support the remodeling and restructuring of connective tissue and modulate the expression of many genes, including the regulation of TGF-β pathway genes. In this way, NL-GHK-Cu has been shown to reverse the expression of key genes contained in the gene signature of COPD, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The expression of 127 genes was altered in patients with COPD. More severe symptoms of emphysema were correlated with the degree of gene expression change. Genes whose expression was associated with inflammation were increased, while genes involved in tissue remodeling and repair were significantly decreased. NL-GHK-Cu is a peptide that can reverse changes in gene expression associated with the destruction of emphysema, such as reduced activity of genes involved in the TGF-β pathway, in such a way that under the influence of NL-GHK-Cu, it was able to change the gene expression pattern to its opposite by activating the TGF-β pathway. NL-GHKCu may also have a beneficial effect on connective tissue. Lung fibroblasts derived from COPD patients, which had impaired collagen contraction and restructuring abilities, were treated with NL-GHK-Cu or TGF-β therapy. Both molecules restored fibroblast function and increased integrin beta 1 expression.
PROTECTIVE AND SAFEGUARDING ROLE OF NL-GHK-CU
The use of the NL-GHK-Cu peptide protects lung tissue from acute lung injury (ALI) and inhibits the migration of inflammatory cells into the lungs. The NL-GHK-Cu peptide also increased superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity while reducing TNF-1 and IL-6 production by blocking NFκB p65 and p38 MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) activation. Mitogen-activated protein kinases are kinase enzymes that play a key role in cell signaling. P38 MAPK pathways enable cells to respond to a wide range of external stressors and influence skin differentiation, apoptosis, mobility, and gene expression, demonstrating that NL-GHK-Cu peptide therapy has a protective effect on the respiratory system in the human body.
Bibliography
- Park JR, Lee H, Kim SI, Yang SR. The tri-peptide GHK-Cu complex ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Oncotarget. 2016;7(36):58405-58417. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.
- W Ma, M Li, H Ma, W Li, L Liu, Y Yin, X Zhou, G Hou.Protective effects of GHK-Cu in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via anti-oxidative stress and anti-inflammation pathways 2019. 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117139
- Pickart L, Margolina A. Regenerative and Protective Actions of the GHK-Cu Peptide in the Light of the New Gene Data. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(7):1987. Published 2018 Jul 7. doi:10.3390/ijms19071987
- Michajlik A. Anatomia i fizjologia człowieka. Wydawnictwo PZWL.2009.





The anti-aging role of NL-Epithalon as a longevity-promoting peptide
NL-GHK-Cu in the nervous system